Hualapai Valley Hydrologic Model: Presentation Date: 10/19/2020
Hualapai Valley Hydrologic Model
Jake Knight & Jamie Macy
Arizona Water Science Center
Problem
- Expanding groundwater withdrawals in Hualapai Basin could impactthe City of Kingman, AZ municipal water supply
Objective
- Assess impacts from additional groundwater withdrawals and enhanced recharge in Hualapai Basin
Approach
- Groundwater Monitoring
- Groundwater Modeling
Setting and Previous USGS Studies
Prior to ADWR Rural Watershed Initiative Program there was very little information known about Hualapai, Detrital, and Sacramento Basins
USGS studies from 2007-2013 laid the foundation
- Changes in groundwater levels over time
- Groundwater withdrawals within each basin
- The geometry of the basins and subbasins
- The basin characteristics – types of sediments and location
- The water budget
- A preliminary numerical model
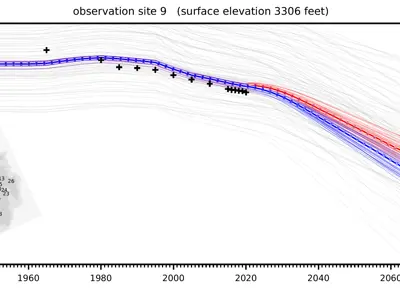
Model Purpose and Forecast Strategy
- The purpose of HVHM is to forecast the potential effects of groundwater withdrawals and enhanced recharge in the Hualapai Valley Basin, based on scenarios provided by Mohave County.
- Forecasted conditions are intended to be conservative with regard to uncertainty.
- Model development decisions were driven by the model purpose.
- The end product is a mixture of simplicity and complexity. The model grid, stress inputs, and time discretization scheme are relatively simple, while the parameterization scheme is highly detailed.
USGS and ADWR Withdrawal Scenario Comparison
- USGS scenario = 128,800 acre-ft/yr (Mohave County developed scenario)
- USGS max 44,000 acres in production
- ADWR scenario A = 280,000 acre-ft/yr
- ADWR scenario B = 340,000 acre-ft/yr
- ADWR max 57,000 acres in production
Future Withdrawal PLUS Enhanced Recharge Scenario
| Map ID | Project Name | Existing (ac-ft/yr) | Planned (ac-ft/yr) |
| 1 | Kingman treated wastewater recharge | 1,200 | |
| 2 | Kingman Monsoon Park at Southern & Eastern Ave | 10 | |
| 3 | Kingman Southern Vista & Hualapai Shadows subdivisions storm water basins | 109 | |
| 4 | Kingman Hualapai Foothill subdivision washes | 82 | |
| 5 | Kingman Rancho Satna Fe washes | 50 | |
| 6 | Kingman SE area BLM Lan infiltration basins | 178 | |
| 7 | Kingman Rattlesnake Wash infiltration basins | 510 | |
| 8 | Kingman West area infiltration basins | 93 | |
| 9 | Peacock Nuts LLC Property basins (8 basins) | 1,693 | |
| 10 | Bank Street, High School infiltration project | 200 | |
| 11 | Mohave Wash N of Thompson Ave basin and recharge well | ||
| Total | 1,210 | 3,915 |
Kingman Subbasin Timing
ADWR
- Scenario A below 1,200 ft bls in 2080
- Scenario B below 1,200 ft bls in 2078
USGS
- Scenarios simulate 650-725 ft bls near Kingman supply wells in 2050
- Scenarios simulate 750-850 ft bls near Kingman supply wells in 2080
Hualapai Subbasin Timing
ADWR
- Scenario A below 1,200 ft bls in 2098
- Scenario B below 1,200 ft bls in 2090
USGS
- Scenarios simulate 550-625 ft bls in 2050
- Scenarios simulate 650-725 ft bls in 2080
Model Summary
Groundwater to wells overwhelmingly from storage - mining
Timing, location, & magnitude of increased pumping most important aspects controlling forecasts
Kingman and Hualapai Subbasins will become less hydraulically connected, potentially totally disconnected. Monitoring important.
Model cells representing thinnest basin-fill material on perimeter of basin go dry in model simulations, but these areas are not the focus of the model forecasts.
Model projections show groundwater available at municipal supply wells beyond 2080